class iii malocclusion slideshare
3-5 UK -IN ASIAN POPULATION. Class iii malocclusion slideshare Thursday March 31 2022 Edit.
Orthodontic Dr Enas Talb 4th Class Ppt Video Online Download
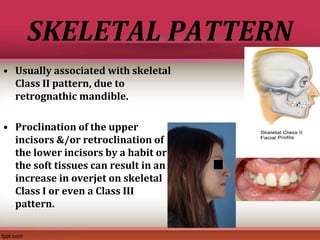
Skeletal Class III patients can be treated by either orthopedics orthodontic camouflage or orthognathic surgery depending on the degree of skeletal discrepancy the skeletal pattern and the age of the patient.

. VTs GROWTH IN PATIENTS WITH CLASS IIIGROWTH IN PATIENTS WITH CLASS III MALOCCLUSIONSMALOCCLUSIONS The craniofacial skeletal pattern of children with ClassThe craniofacial skeletal pattern of children with Class III malocclusion is evident in the early deciduousIII malocclusion is evident in the early deciduous dentitiondentition. Khushbu Agrawal Guided by. Class III malocclusion seminar 1.
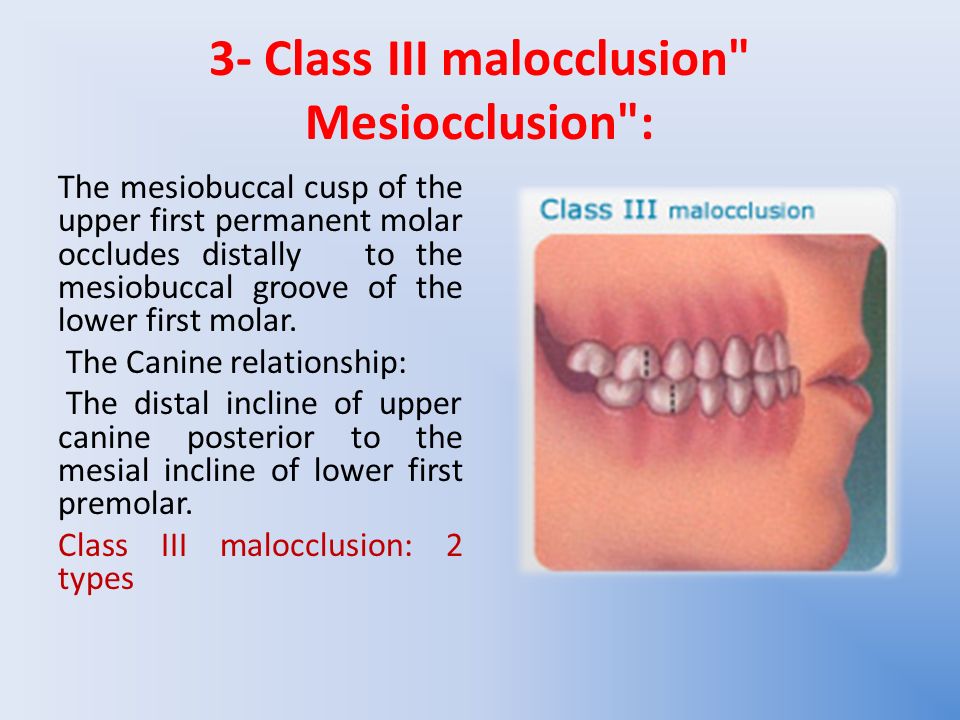
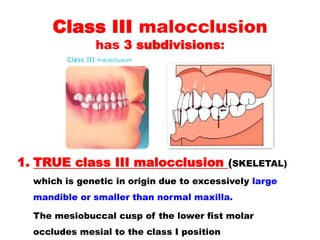
CLASS III SUB-DIVISION Condition in which class III molar relationship is present only on one side with normal relation on the other side. Maxillary and mandibular skeletal and dental components which necessitate precise Orthognathic surgical. PSEUDO CLASS III MALOCCLUSION Due to occlusal prematurity when the mandible moves from rest position to occlusion it slides forward into a pseudo class III position.
56 The prevalence is greater in Asian populations. Share yours for free. Clinicians have been trying to identify the best timing to intercept a Class III malocclusion that develops as early.
Class III malocclusions are the least common type of malocclusion yet they are often more complicated to treat and more likely to require orthognathic surgery for optimal correction. A sample of 69. CLASS III MALOCCLUSION Presented by.
The dental compensation presented in patients with the Class III malocclusion or mandibular prognathism and its importance to the surgical-orthodontic treatment was evaluated in this study. Class III malocclusion is a less frequently observed clinical problem than Class II or Class I malocclusion occurring in less than 5 of the US. Evolution of Class III treatment in orthodontics Peter Ngana and Won Moonb Morgantown WVa and Los Angeles Calif Angle Tweed and Moyers classified Class III malocclusions into 3 types.
The study involved the cephalometric examination of two groups of patients who were considered either adeq. Class II malocclusion. The mandible and mandibular incisors are then guided anteriorly in central occlusion resulting in an anterior crossbite.
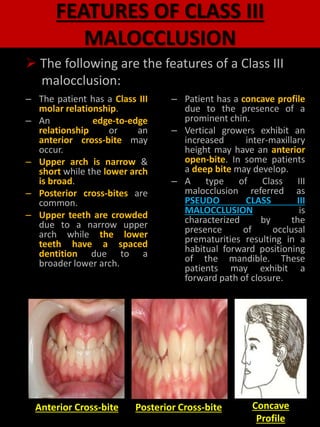
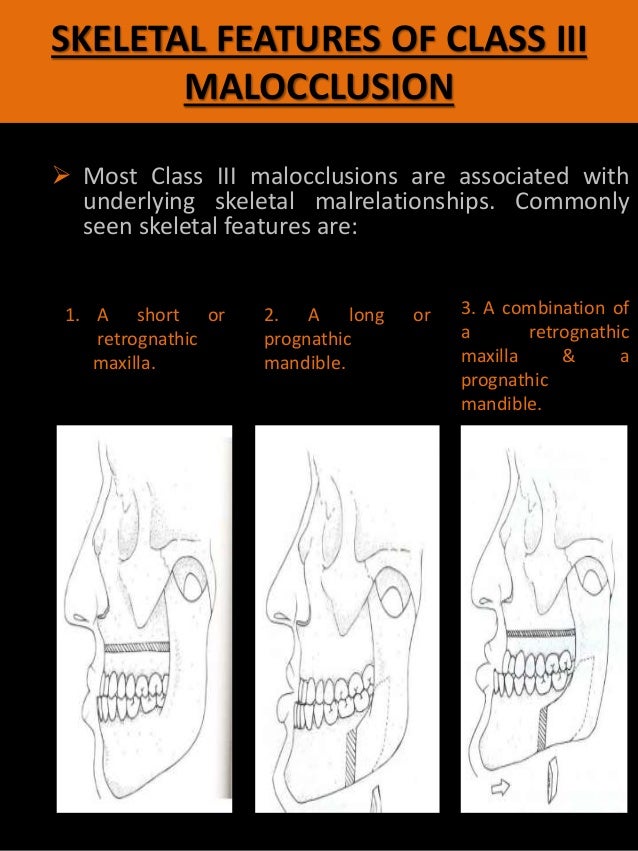
Its also known as postural class III. Class III malocclusion is considered to be one of the most difficult and complex orthodontic problems to treat. The Skeletal Class III malocclusion is characterized by mandibular prognathism maxillary deficiency or both.
CONTENT INTRODUCTION CLASSIFICATION ETIOLOGY CLINICAL FEATURES DIAGNOSIS TREATMENT 3 3. Treatment by maxillary protraction is. Pression of what appears to be a true skeletal Class II malocclusion.
1 The reported incidence of this malocclusion ranges between 1 to 19 with the lowest among the Caucasian populations 23 and the highest among the Asian populations. In addition to distal step molar relation or an unusu-ally large overjet tooth size discrepancy with or without malrelated mandible and maxilla may also give the first impression of a true skeletal Class II malocclusion. Learn new and interesting things.
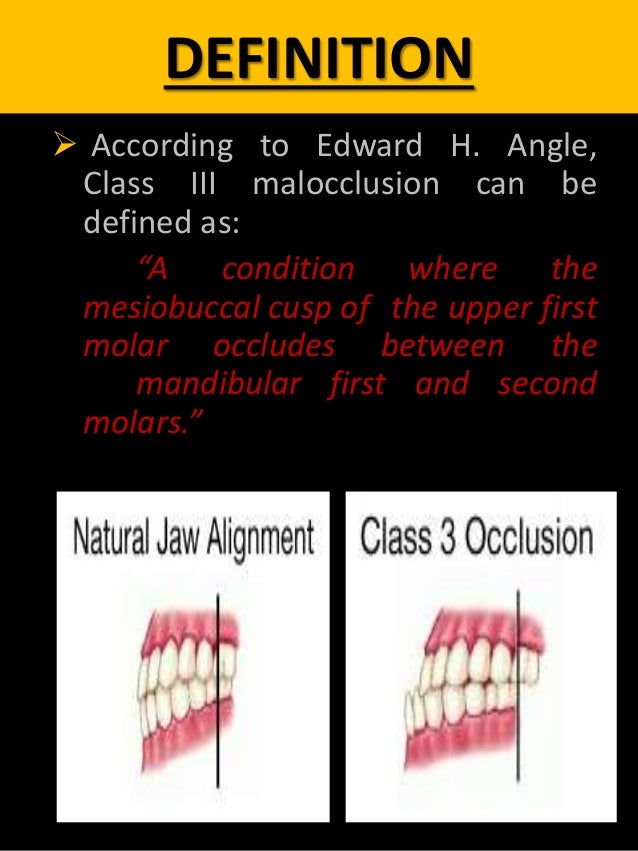
Pseudo dentoalveolar and skeletal. Class III Prognathism also known as underbite is a malocclusion caused by the lower teeth being positioned further forward than the upper teeth. The lower lip is often protruded relative to the upper lip.
Adult Skeletal Class III Malocclusion is one of the most severe and difficult to correct Maxillofacial deformities2 involving multiple complex inter-related aspects such as cranial base abnormalities. Surgical treatment of Class III malocclusion includes in most cases mandibular retrusion maxillary protrusion or a combination of both. -Class III incisor.
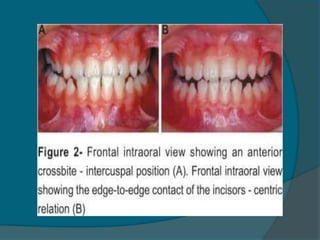
Is when the lower incisor edge lies anterior to the cingulum plateau of the upper incisors. Home iii malocclusion slideshare wallpaper. Anterior crossbite with functional shift also called pseudo Class III is a malocclusion in which the incisal edges of one or more maxillary incisors occlude with the incisal edges of the mandibular incisors in centric relationship.
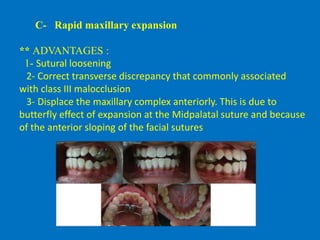
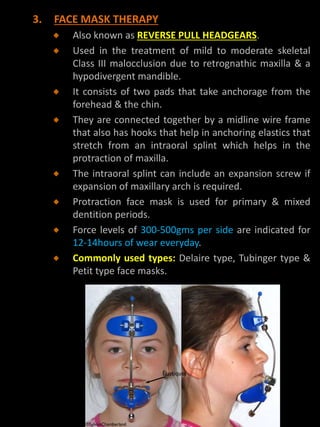
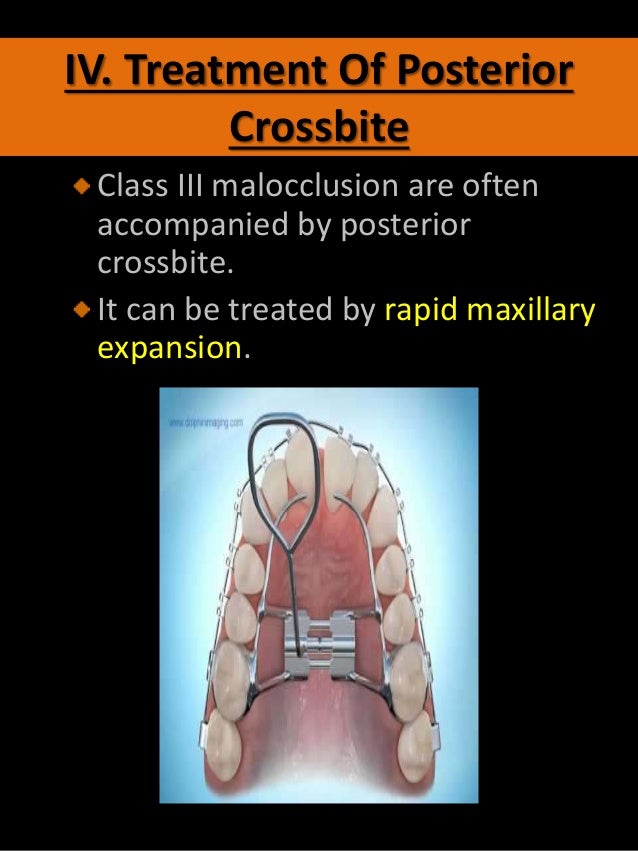
The purpose of this study was to analyze the cephalometric changes that occurred during and after the correction of Class III malocclusion. The choice of treatment options of Class III malocclusion depends on the age of the patient the pattern of malocclusion and the severity of malocclusion. The orthopedic approach for growth modification is usually limited to children with growth remaining.
The records of 24 Class III patients treated with a banded expansion appliance and custom facemask were compared with 24 Class I and 27 Class III untreated controls. Class III malocclusions are the least common type of. Class Ii Malocclusion Group Ppt Video Online Download Class Iii Malocclusion Class Iii Malocclusion Class Iii Malocclusion 100 Malocclusions Common Orthodontic Problem Mohamad Aboualnaser Awat Class 3 Malocclusion.
Prevalence of class III malocclusion in Caucasians ranges from 08 to 40 and rises up to 1213 in Chinese and Japanese populations while in North Indian population class III malocclusion is found in up to 34 of the population. Clinically these patients exhibit a concave facial profile a retrusive nasomaxillary area and a prominent lower third of the face. The embrasure between the lower canine and the lower first premolar is shifted forward with regard to the upper canine blue arrows.
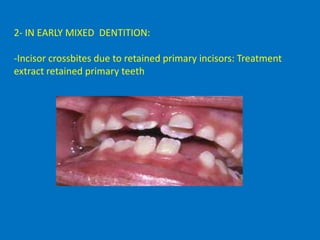
Mandibular clockwise rotation can also provide the same result as mandibular retrusion when increase. The center of the lower first molar mesiobuccal groove is anterior to. Pseudo Class III Malocclusion Pseudo class III malocclusion is a habitual established cross bite of all anterior teeth without any skeletal discrepancy resulting from functional forward positioningshift of the mandible on closure.
It is where an anterior displacement masking an underlying sk class I base. View Class 3 Malocclusion PPTs online safely and virus-free. The American Veterinary Dental College defines Class II malocclusion as mandibular distocclusion when there is an abnormal rostro-caudal relationship between the dental arches in which the mandibular arch occludes caudal to its normal position relative to the maxillary arch Figure 3Terms that have commonly been associated with class II.
Class III A class III intermaxillary relationship means that the lower teeth are shifted forward with regard to the upper teeth. Get ideas for your own presentations. Prevalence of class III malocclusion in Caucasians ranges from 08 to 40 and rises up to 1213 in Chinese and Japanese populations while in North Indian population class III malocclusion is found in up to 34 of The upper teeth are more advanced compared to the lower teeth a 11-mm overjet and we can easily see that the lower incisors touch the palate at the back of the upper.
The estimated incidence of Class III malocclusion among the Korean Japanese. Peter Ngan Hong He in Current Therapy in Orthodontics 2010. 10 IN CHILDREN 4.
8 Setting Of Teeth For Class I Ii And Ii Arch Relation Ship Edit
Classification Of Malooclusion
Classification Of Orthodontic Malocclusion Ppt Download
Classification Of Malocclusion

Class Iii Malocclusion Ppt Download